INSIGHTCLOUDSEC
Eliminate Cloud Risk. Automate Compliance.
- Monitor cloud risk everywhere, in real time
Detect cloud risk immediately with real-time, agentless visibility into everything running across your entire environment. - Prioritize risk with layered context
Know exactly which risk signals to prioritize thanks to complete context, with the broadest and deepest coverage across major cloud platforms. - Automate cloud compliance any way you need
Enforce organizational standards, streamline the remediation process, and fix compliance drift immediately with native, no-code automation.
Reduce organizational risk
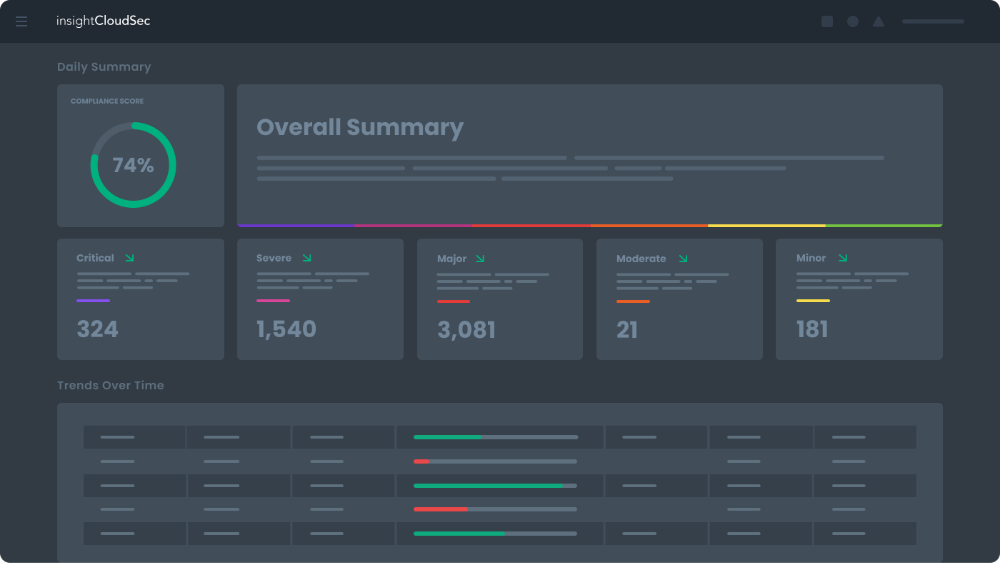
Stop playing whack-a-mole with never-ending risk signals and alerts. Track progress in improving organizational compliance and risk posture.
Improve team efficiency and cross-team collaboration
Make collaborating with stakeholders across your organization a breeze through seamless integration with your existing tools and processes.
Consolidate your cloud security tool set
Forget niche point solutions that only solve a sliver of the problem. InsightCloudSec provides a unified platform that meets all of your cloud security needs with a single subscription.
Accelerate mean time to respond (MTTR)
Respond to cloud risks faster than ever with real-time risk detection, intelligent prioritization, and automated remediation workflows, limiting blast radius and business impact.

Key Features
InsightCloudSec is a fully-integrated cloud-native security platform—your whole cloud security toolbox in a single solution.
- Real-Time Visibility Across Clouds
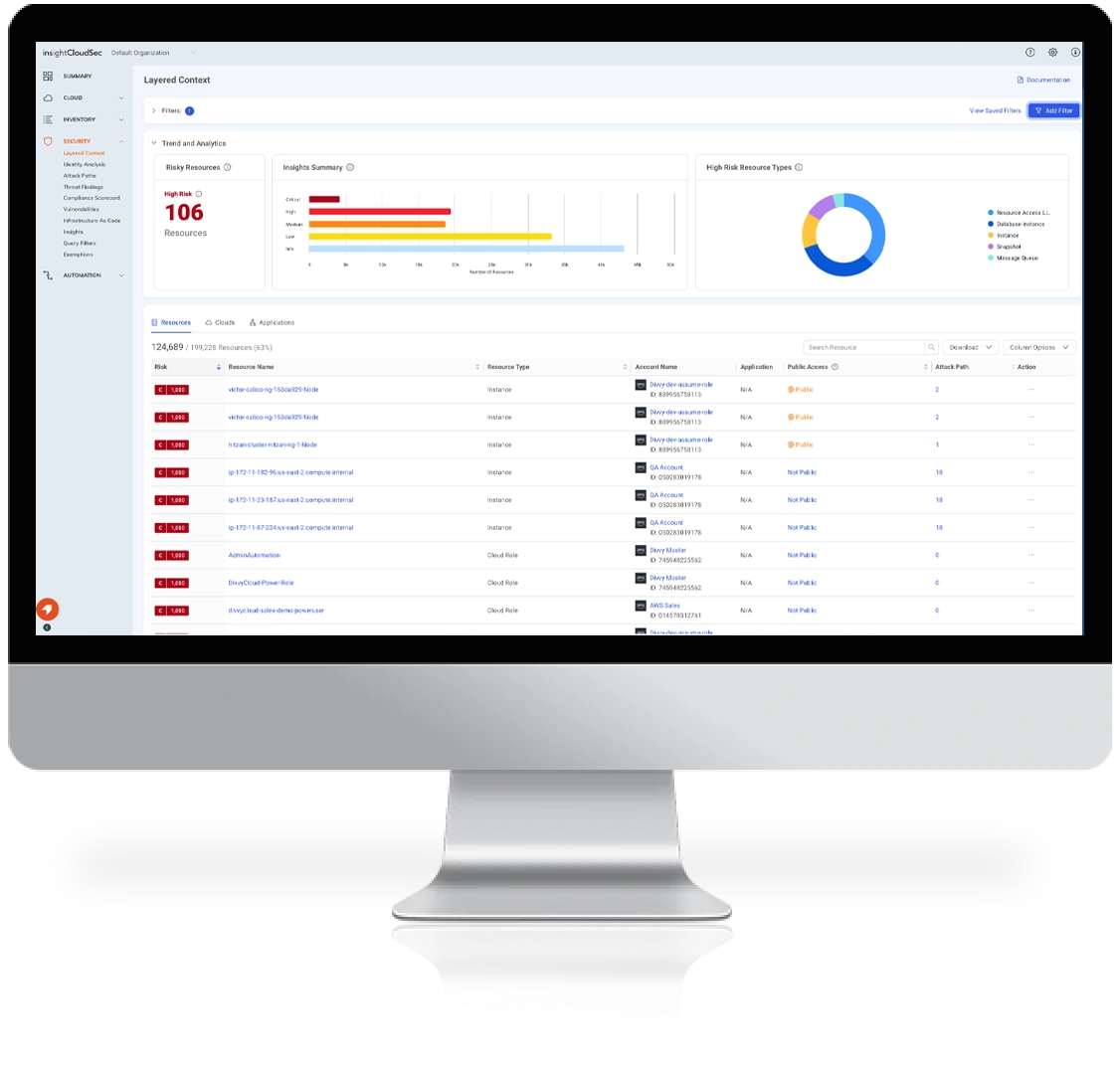
- Context-Driven Risk Management
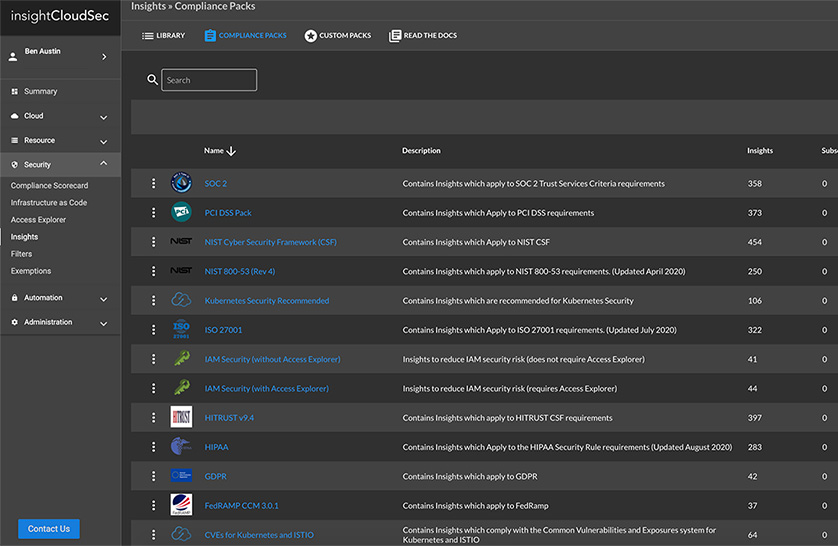
- Cloud Compliance Management
- Agentless Vulnerability Management
- Cloud Infrastructure Entitlements Management (CIEM)
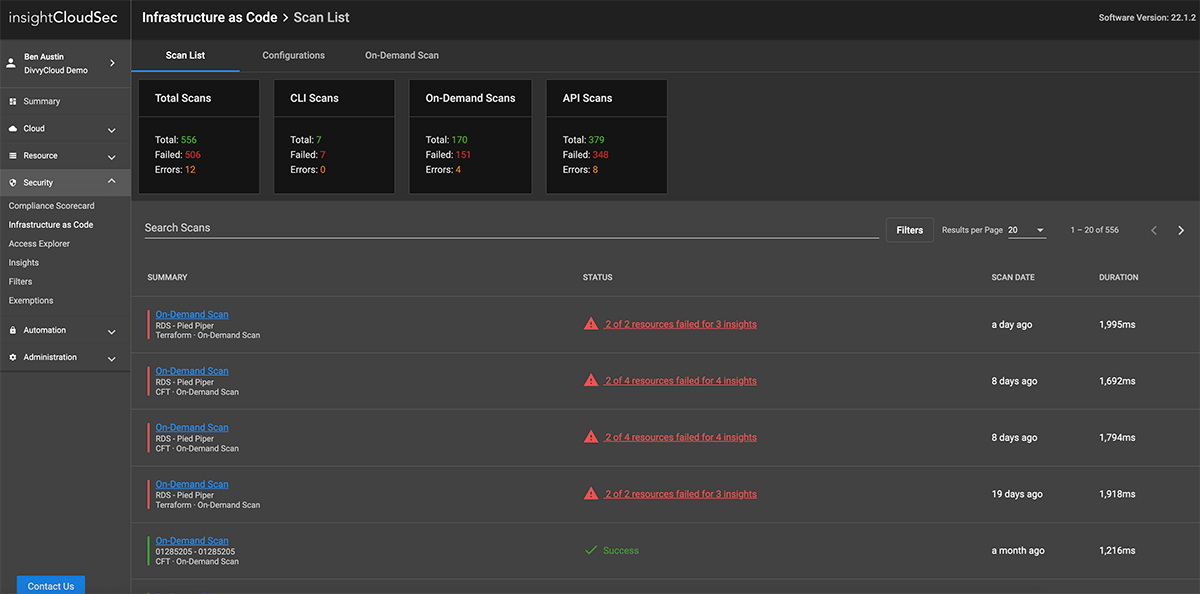
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Security
- Automation and Real-Time Remediation
- Kubernetes Security Guardrails
- Cloud Detection and Response (CDR)
- Cloud Hygiene and Cost Containment
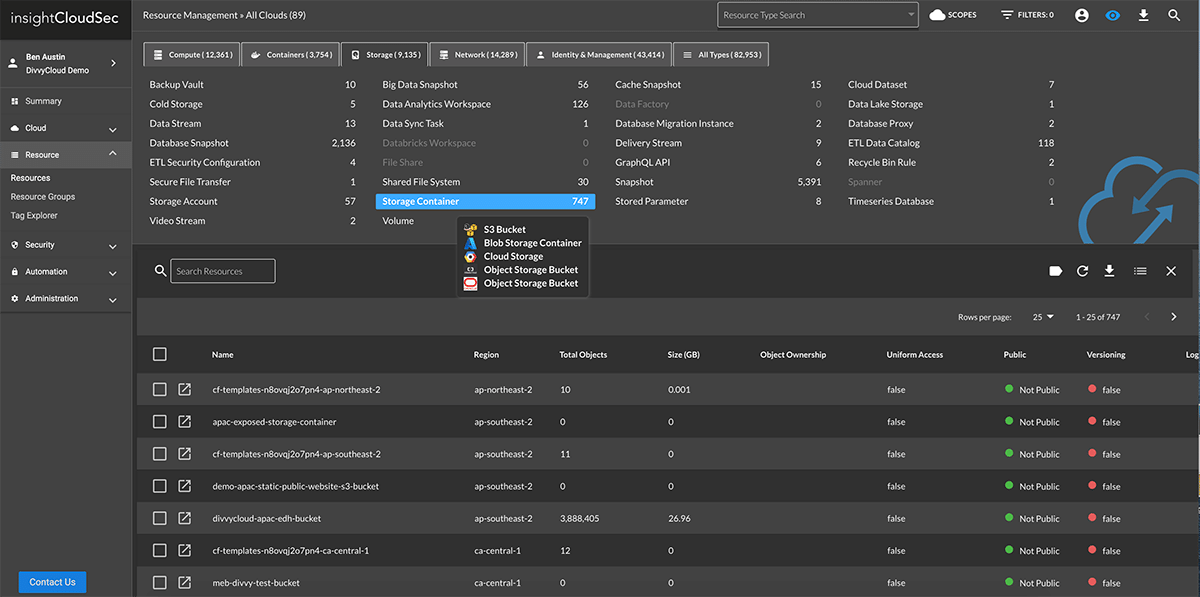
See All Cloud Assets In One Place
Enterprises are using the cloud to drive innovation and digital transformation. However, most security and operations teams lack unified visibility into the various cloud services being used by their development teams. InsightCloudSec lets you continuously monitor all your cloud and container services in one user-friendly platform with better insights into associated risks.
Learn MoreSurface and Assess Cloud Risks in Real Time
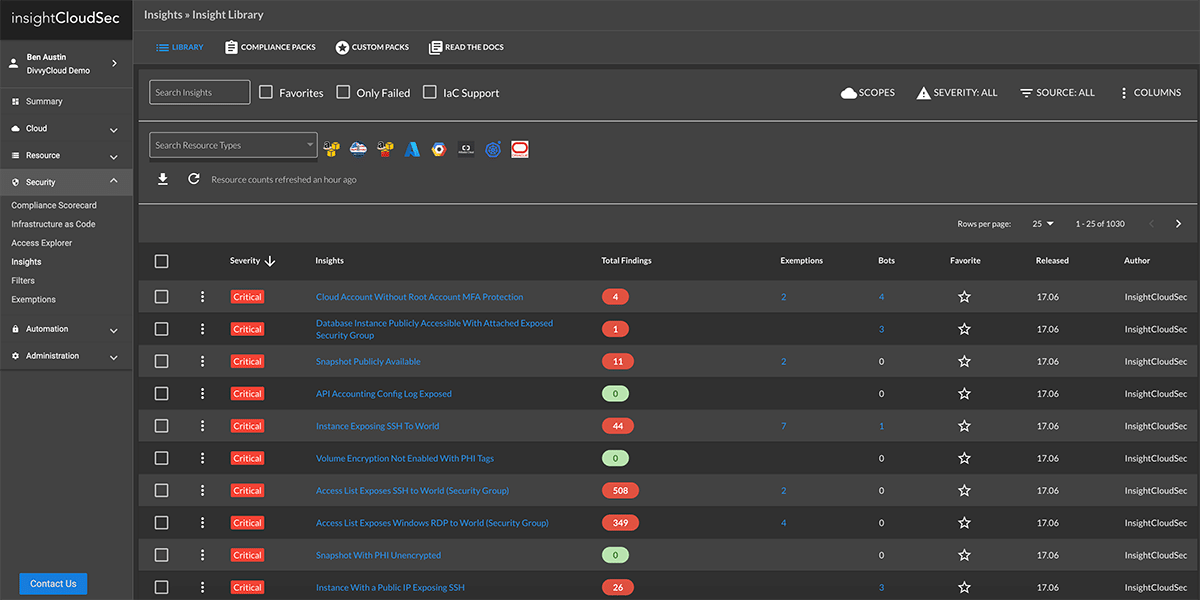
It’s common to be overwhelmed with a large volume of threat signals from various resources, making it hard to identify true risks and act on them in a timely fashion.
InsightCloudSec enables up-to-the minute cloud risk assessment by providing full context across the infrastructure, orchestration, workload, and data tiers.
Learn MoreApply Consistent Policies to Prevent Misconfigurations
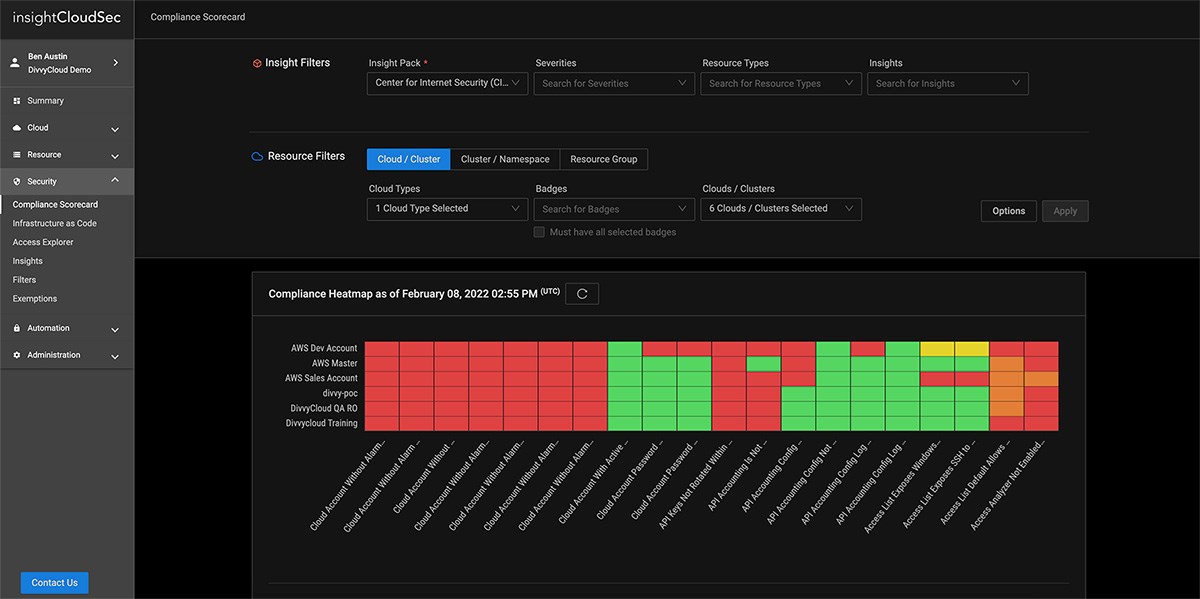
As organizations navigate their digital transformation, security teams are tasked with mitigating risk and maintaining compliance across massive, ever-changing multi-cloud environments.
InsightCloudSec standardizes your entire asset inventory across multiple cloud service providers so you can consolidate policy management and leverage automated remediation to consistently eliminate unwanted or non-compliant configurations no matter where they turn up.
Learn MoreSimplify Identity and Access Management
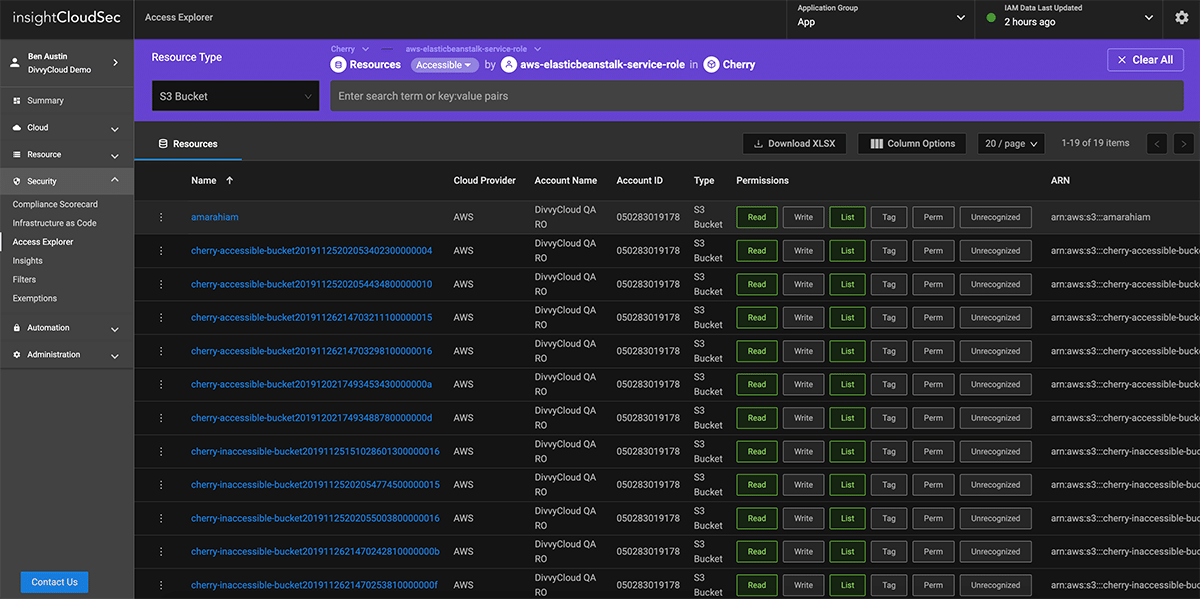
In cloud environments, everything has an identity: users, applications, services, and systems. This provides enormous flexibility, but also creates the potential for substantial risk as every service is potentially reachable by every other one.
InsightCloudSec helps organizations adopt a least-privilege access model by proactively analyzing cloud environments for excessive entitlements at scale.
Learn MoreShift Your Cloud Security Program Left
As Security and DevOps teams continue to work together, organizations need a way to consistently evaluate risk earlier in the CI/CD pipeline so they can prevent problems before they happen, speed up developer efforts, and reduce friction.
InsightCloudSec enables security teams to provide a single, consistent definition of good across the full CI/CD pipeline, allowing you to evaluate potential risks of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) templates before they are built or deployed.
Learn MoreCoverage for all major cloud service providers, including: